How Sound Waves Find 2 Applications in New Powerful Surgical Equipment
February 25, 2025 2025-02-26 6:50How Sound Waves Find 2 Applications in New Powerful Surgical Equipment
How Sound Waves Find 2 Applications in New Powerful Surgical Equipment
With the high-speed era of surgery, minimality and precision are of paramount concern when it comes to innovation. One of the most revolutionary changes in recent history has possibly been the application of sound waves—that is, the use of ultrasound technology—in surgical equipment.
Sophisticated tools such as ultrasonic scalpels and cavitation-assisted surgical devices use high-frequency sound to remove tissues, close blood vessels, and even remove tumors with unprecedented accuracy. These innovations are transforming surgical procedures by minimizing collateral tissue damage, lessening blood loss, and allowing for quicker patient recovery.
This is the science of ultrasonic surgical instruments, their benefits, and how they are transforming medicine today.
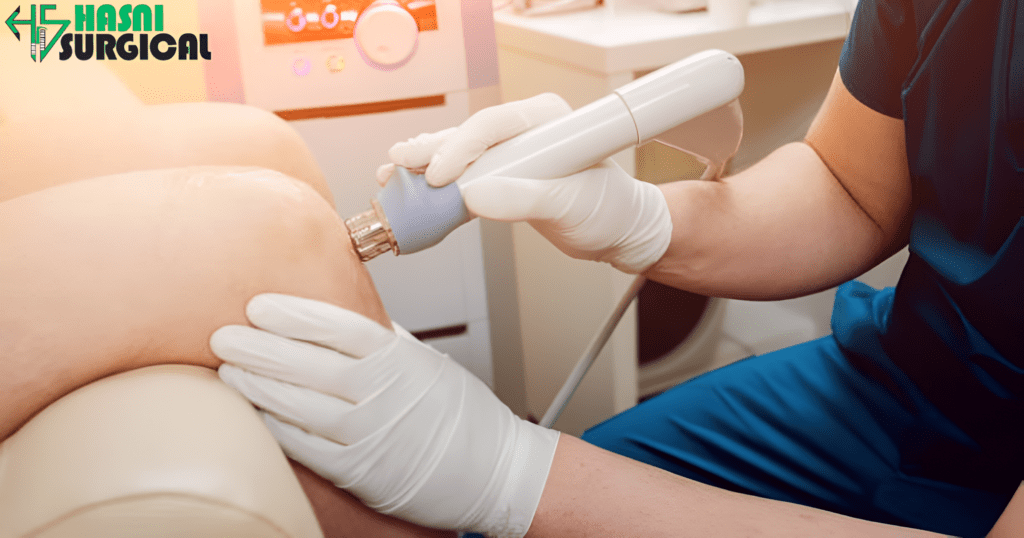
Knowing ultrasonic surgical instruments and What Sound Waves are in Surgery
Sound waves refer to mechanical vibrations that propagate in a medium (air, water, or tissue). During surgery, however, ultrasound waves with frequencies higher than 20,000 Hz, beyond audible human hearing, are employed to create mechanical energy that can break or cut up tissues at the microscopic level.
Ultrasonic energy has been utilized for many years in medical imaging (e.g., ultrasound scans), but as an aid to surgery, it is relatively recent. Equipment based on focused ultrasound, cavitation, and harmonic vibration is changing the manner in which precise surgical interventions are conducted, especially in oncology, neurosurgery, and minimally invasive interventions.
Surgical Instrument and their Uses
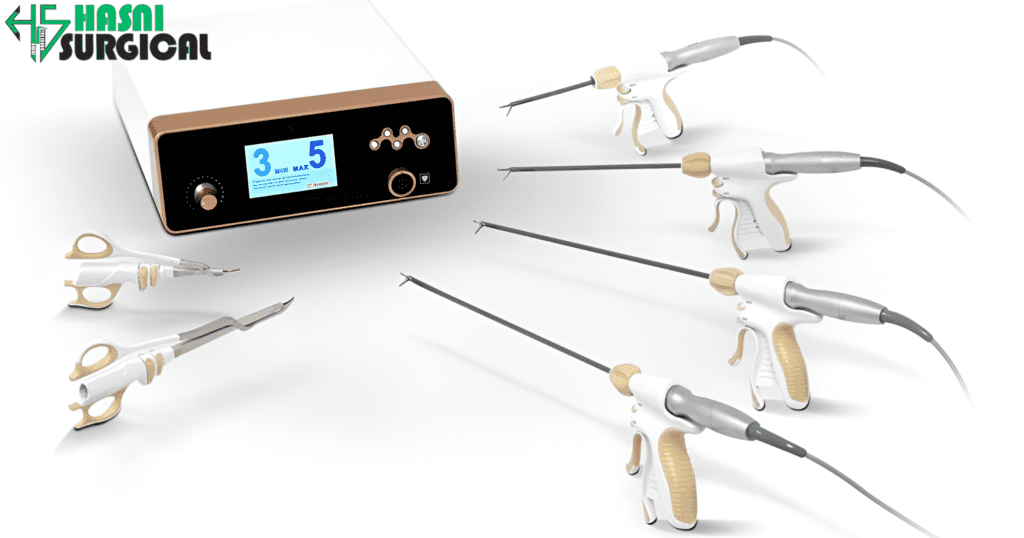
Ultrasonic Scalpels: The Way to High-Precision Cutting
The most widely used ultrasonic surgical tool is the ultrasonic scalpel. In contrast to traditional scalpels, which use sharp blades to incise tissue, ultrasonic scalpels use ultrasonic high-frequency vibrations to create heat and mechanical energy that precisely cut tissue along with coagulating blood vessels.
Functioning of Ultrasonic Scalpels
An ultrasonic scalpel contains:
- A transducer that converts electrical energy to ultrasonic vibration (usually 20 kHz to 60 kHz).
- A rapidly vibrating blade or probe, used to dissect soft tissues with high accuracy.
- A frequency controller, power source, and intensity controller that controls frequency, power, and intensity.
- When used in tissue, the ultrasonic vibrations create high-frequency vibration of water molecules within the cells, generating frictional heat that cuts and coagulates simultaneously. Ultrasonic scalpels are thus well-adapted for minimally bleeding operations, like thyroidectomy, laparoscopic surgery, and oncologic resections of tumors.
Key Benefits of Ultrasonic Scalpels
- Minimal Thermal Spread: In contrast to conventional electrosurgical devices with high heat (e.g., cautery), ultrasonic scalpels cut at lower temperatures (usually less than 100 °C). This minimizes the risk of collateral tissue damage and burns.
- Less Blood Loss: Because ultrasonic scalpels also cauterize vessels when they cut, they have a cleaner operating field and less need for unnecessary suturing or cauterization.
- Accuracy and Control: The regulated vibrations provide the ability to become more accurate, which is intensified for more sensitive procedures near nerves, blood vessels, or other sensitive tissue.
- Reduced Operating Time: Since coagulation and cutting are combined into one step, ultrasonic scalpels reduce procedure time, leading to a decreased operating time and faster recovery for patients.
Applications of Ultrasonic Scalpels
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Used in gallbladder removal, colorectal surgery, and gastric bypass.
- Oncology Surgery: It allows for tumor resections wherein precision and least blood loss are of the utmost concern.
- ENT and Head & Neck Surgery: Used in thyroid surgery and tonsillectomy.
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery: Used in delicate soft tissue surgeries.

Cavitation-Assisted Surgery: Accurate Surgery through Microbubbles
Another new application of sound waves in surgery comes through cavitation-assisted surgical equipment. Cavitation involves the process wherein ultrasound waves create minute vapor bubbles within an aqueous environment. On their breakdown, they release high mechanical energy that will either disperse tissues, kill tumors, or dissolve blood vessel blocks.
How Cavitation-Assisted Surgery Works
Cavitation-assisted surgical instruments generally work in two primary ways:
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): Utilizes focused waves of ultrasound to induce cavitation in tissues and selectively destroy undesired structures such as tumors with minimal open surgery.
- Ultrasonic Aspiration Devices: Apply cavitation for soft tissue fragmentation and thus find application in neurosurgery, tumor resections, and liver resections.
The accurate release of energy via cavitation provides selective tissue ablation with the least possible injury to the adjacent structures and thereby is a clear contender for non-invasive and minimally invasive surgeries.
Chief Benefits of Cavitation-Assisted Surgery
- Targeted Tissue Destruction: Cavitation can be selectively controlled to destroy the targeted tissue only without harming adjacent tissues.
- Non-Surgical Treatment Techniques: Methods like HIFU allow tumor destruction without any requirement for cuts, reducing patient suffering and recuperation.
- Less Scarring and Trauma: Since cavitation-based therapies result in minimal disruption to tissues, scarring and side effects post-surgery are minimized.
- Several Applications: Cavitation-guided surgery has the application from oncology to cardiovascular surgery and offers safer methods over conventional methods.
Routine Applications of Cavitation-Assisted Surgery
- HIFU Treatment of Tumors: Used in the treatment of prostate cancer, liver tumor, and uterine fibroids.
- Neuro-Surgery: Ultrasonic aspirators are used for tumor removal in brain tumors with preservation of crucial structures.
- Liver & Kidney Surgery: Offers precise removal of tissue with minimal blood loss.
- Cardiovascular Surgery: Used to clear obstructions from arteries without surgery.

The Future of Ultrasonic Surgical Equipment
The future of ultrasonic and cavitation-driven surgical equipment is bright with the increasing technology in the fields of ultrasound physics and surgery engineering. The excitement today includes:
- Robot-Assisted Ultrasonic Surgery: The merge of roboticexterity with ultrasonic scalpels to make it easier to perform precise microsurgical operations.
- Advanced HIFU for Cancer Treatment: Novel technology is under investigation to employ ultrasound waves to cause targeted drug release for chemotherapy.
- Personalized Cavitation Therapy: Automatically intelligent ultrasound machines would be capable of adjusting treatment levels for individual patients for optimal outcomes.
They could reduce future surgery to be safer, more effective, and less invasive.
Conclusion
The age of modern surgery is now being revolutionized through the aid of sound waves, which are making it safer, more precise, and less invasive than ever before. Ultrasonic scalpels create bloodless, high-definition cuts, and cavitation-assisted technology allows non-invasive tissue ablation with little collateral damage.
These devices are already found to be of great value in oncology, neurosurgery, and minimal invasive surgery and in improving the surgical capacity of the patient and the recovery. With the development of technology, ultrasonic and cavitation-enhanced surgery will be further improved, and future therapy will be safer and more effective.
The future of surgery is healthy—literally.
