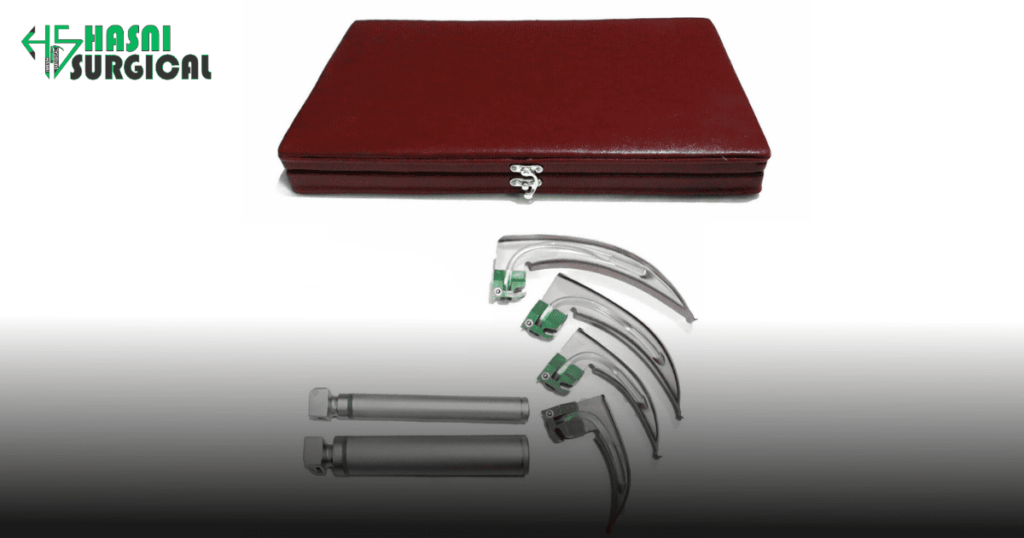
Challenges and Solutions in Laryngoscopy procedure
June 13, 2024 2025-01-02 11:59Challenges and Solutions in Laryngoscopy procedure

Challenges and Solutions in Laryngoscopy procedure
Laryngoscopy procedure
Introduction:
A laryngoscopy procedure is a vital medical procedure used for visualizing the larynx, or voice box, typically for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. It plays a key role in medical fields like ENT, anesthesia, emergency medicine, and critical care. The procedure uses a lighted laryngoscope to examine the larynx.
Addressing these is essential for optimizing outcomes and ensuring effective patient care. These challenges can impede successful visualization of the larynx, leading to diagnostic delays, treatment complications, or even life-threatening situations.
This post covers challenges in laryngoscopy procedures and solutions to improve safety and patient outcomes.
Challenges in laryngoscopy procedure:
These challenges can arise from various factors, including patient anatomy, equipment limitations, operator experience, and clinical scenarios.
1. Limited Mouth Opening: Patients with restricted mouth openings from temporomandibular joint disorders, trauma, or congenital conditions can complicate laryngoscopy procedures. This restriction may obstruct laryngoscope insertion and larynx visualization, necessitating alternative techniques or specialized equipment for airway management.
2. Obesity and neck immobility can obscure landmarks and limit neck movement, complicating laryngoscopy procedures. This may require adjustments in technique and equipment.
3. Adequate illumination of the oral cavity and pharynx is critical for enhancing visualization and ensuring safe and effective airway management.
4. Proper patient positioning is crucial for a successful laryngoscopy procedure. Incorrect positioning can hinder laryngeal exposure and raise complication risks. Adjustments to head tilt, chin lift, and neck extension are key to optimizing the view and facilitating airway interventions.
5. Common issues include laryngoscope blade damage, battery depletion, camera malfunction, or inadequate instrument sterilization. Healthcare providers must be prepared to troubleshoot equipment problems promptly and have backup options available to ensure uninterrupted patient care.
8. Inexperienced operators may struggle with laryngoscopy procedures, affecting laryngeal visualization and safe airway interventions. Training, simulation-based education, and ongoing competency assessments are essential for healthcare providers to develop and maintain proficiency in laryngoscopy procedure techniques.
Navigating these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating advanced equipment, innovative techniques, interdisciplinary collaboration, and continuous education and training. In the next section, we will explore the solutions and strategies developed to overcome these challenges and optimize laryngoscopy procedure outcomes.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges:
Healthcare providers have developed techniques, equipment modifications, and protocols to enhance the safety and efficacy of laryngoscopy procedures. Below are some solutions commonly employed to address the challenges of laryngoscopy procedures:
1. Alternative Airway Devices: For difficult airways, use supraglottic airways or video laryngoscopes. These devices offer improved visualization and facilitate airway management in challenging anatomical situations.
2. The fiber-optic laryngoscopy procedure uses a flexible scope to see the larynx clearly, even in difficult airways or challenging cases. This technique helps navigate obstructions and see laryngeal structures clearly in challenging situations.
3. Preoperative assessment and planning are crucial for identifying airway challenges and creating tailored management strategies. This involves reviewing patient history, examining the airway, using imaging, and collaborating with teams to address laryngoscopy procedure challenges.
4. Optimized Patient Positioning: Proper patient positioning is critical for optimizing laryngoscopic visualization and airway management. Techniques like ramped positioning, ear-to-sternal notch positioning, and shoulder rolls improve laryngeal exposure and make intubation easier for challenging patients.
5. Advanced imaging technologies like high-definition cameras, video laryngoscopy procedures, and point-of-care ultrasound improve laryngeal visualization and assist in managing difficult airways. These technologies provide real-time feedback and guidance, enabling healthcare providers to navigate anatomical challenges and optimize airway interventions.
6. Team-based Approach: Collaborative teamwork involving anesthesiologists, otolaryngologists, emergency physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals is essential for a successful laryngoscopy procedure.
7. Ongoing training is essential for healthcare providers to keep laryngoscope procedure skills and airway management knowledge up to date. Simulation-based training, case-based learning, and participation in airway workshops and conferences help enhance technical skills, decision-making abilities, and teamwork dynamics.
8. Maintenance and Quality Assurance: Regular upkeep and checks are crucial for reliable laryngoscopy procedure equipment. Healthcare facilities should implement robust equipment management systems and adhere to manufacturer guidelines for proper instrument care and sterilization.
By adopting these solutions, healthcare providers can improve laryngoscopy procedures and patient outcomes. Continuous innovation, education, and collaboration are crucial for advancing airway management and optimizing laryngoscopy procedures.
Conclusion:
The laryngoscopy procedure is an indispensable procedure in medical practice, enabling healthcare providers to visualize the larynx and manage airway-related conditions effectively. The challenges of laryngoscopy procedure can hinder success, requiring innovative solutions and strategies.
By adopting advanced techniques, upgrading equipment, collaborating, and pursuing ongoing training, healthcare providers can enhance laryngoscopy procedures and improve patient care. Key solutions include alternative airway devices, fiber-optic laryngoscopy procedures, optimized patient positioning, advanced imaging, and team-based approaches for better laryngeal visualization.
A proactive preoperative assessment, rigorous equipment maintenance, and quality assurance are crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring reliable laryngoscopy procedures. By promoting innovation and collaboration, healthcare facilities can improve laryngoscopy procedure outcomes and advance airway management practices.
By focusing on excellence and patient-centered care, they can confidently and effectively navigate laryngoscopy procedures, ensuring safe and effective treatment.

