Transplant Surgeries: The Use of 7 Powerful Surgical Devices
February 21, 2025 2025-02-25 4:33Transplant Surgeries: The Use of 7 Powerful Surgical Devices
Transplant Surgeries: The Use of 7 Powerful Surgical Devices
Organ transplantation is the most sophisticated and life-saving procedure in contemporary medicine and a highly demanding procedure with extreme accuracy, speed, and asepsis to transfer maximum impact for patients. The advancement in surgical devices has enhanced Transplant Surgeries to be more effective by enhancing the chance of the donating organ while accelerating patient recovery.
Here, we are going to describe the significant contribution of advanced surgical tools in organ transplanting, describing the precision tools involved in the complex operations and how they lead to better surgical results.
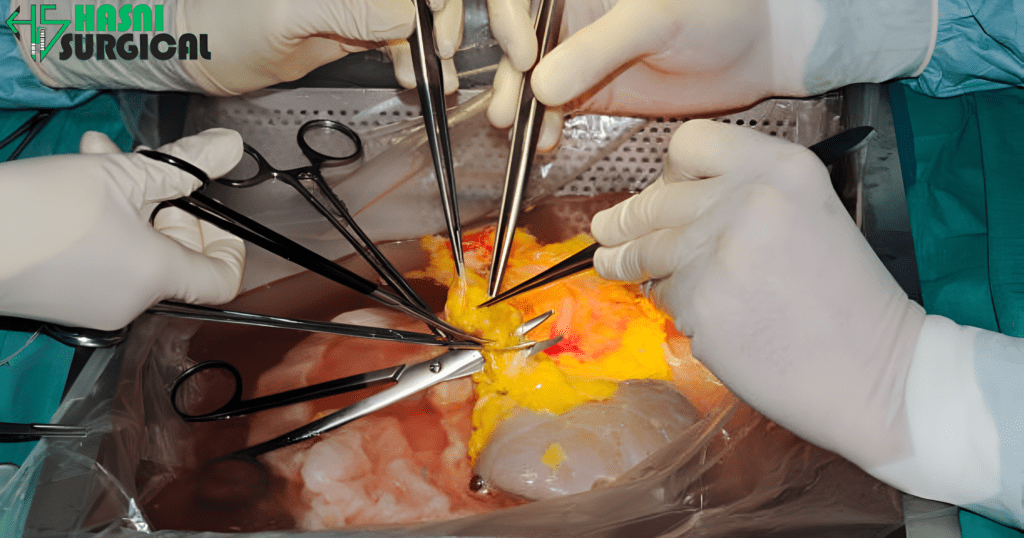
Surgical Instrument and their Uses: The Complexity of Organ Transplant Surgeries
Organ transplantation entails the removal of an organ from a donor and its implantation into a recipient whose organ has failed or is diseased. The most frequently transplanted organs are the kidney, liver, heart, lungs, pancreas, and intestines. Each transplant procedure has unique challenges:
Time sensitivity: Once an organ is harvested, it must be transplanted immediately before it is damaged.
Delicate Tissue Handling: Organs and tissues are fragile and demand a lot of caution.
Microvascular Anastomosis: Repairing blood vessels is done with extreme caution since even a small error can cause complications.
Prevention of Infection: Sterilization is necessary to prevent infection after surgery and organ rejection.
Advances in the surgical devices have addressed these issues, making transplant surgery safer and more successful.
Critical and Powerful Surgical Devices: Organ Transplantation
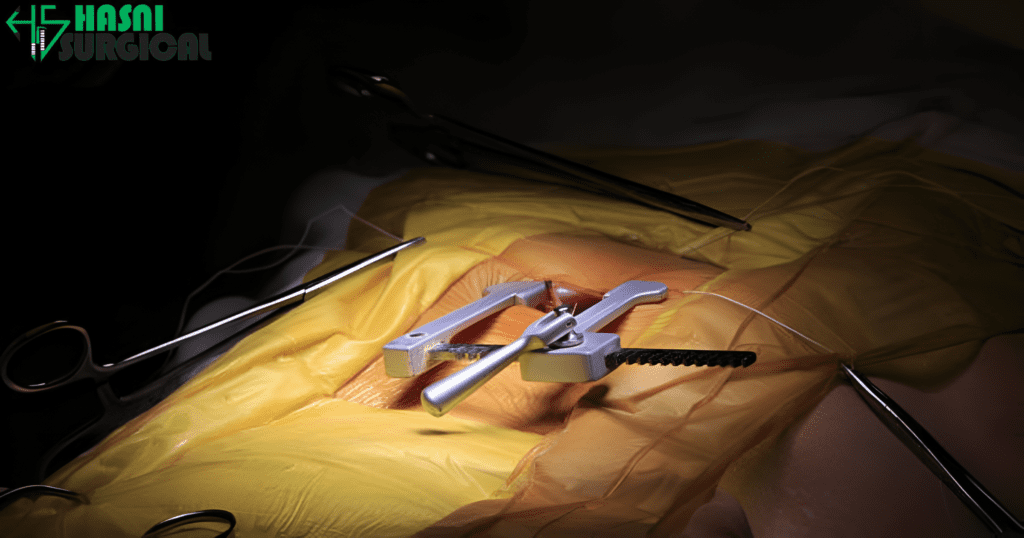
1. Bone Saws and Rib Spreaders
During heart and lung transplants, the chest cavity must be opened carefully. Sternal saws are employed by surgeons to cut through the sternum, while rib spreaders are employed to provide access to the heart and lungs. Modern saws are precision-driven, trying their best not to cause damage to adjacent tissues.

2. Trocars and Cannulas
In laparoscopically assisted organ procurement, trocars and cannulas offer points of entry for surgical tools without the need for extensive incisions. This is particularly useful in kidney and liver transplantation, where minimally invasive techniques improve donor recovery times.

3. Microvascular and Neurosurgical Instruments
Transplantation involves reconnecting the blood vessels with a high success rate. Microforceps, microscissors, and needle holders allow the surgeons to manipulate fine structures without inducing a break. These instruments are crucial in ensuring proper blood supply to the new organ.
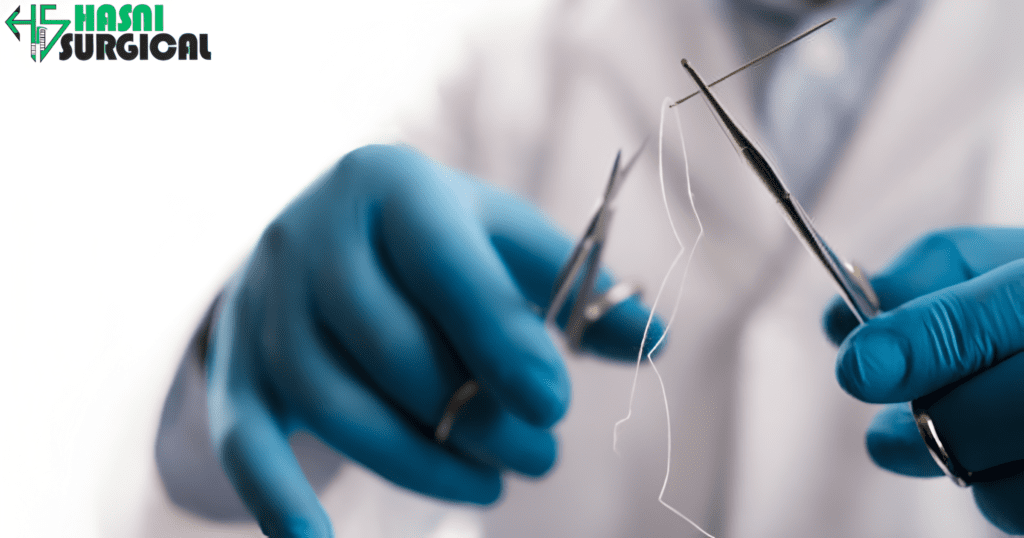
4. Surgical Scissors and Sutures
Acutely sharp surgical scissors aid in dissection and removal of diseased organs. High-quality sutures are used to close arteries and secure the transplanted organ in place. Absorbable sutures reduce the need for secondary surgeries, whereas non-absorbable ones provide long-term stability.

5. Retractors and Clamps
Self-retaining retractors keep the incision open, allowing surgeons better exposure and visibility.
Vascular clamps control blood flow, preventing excessive bleeding when arteries and veins are reconnected.
Bulldog clamps are applied in kidney and liver transplantation to temporarily shut off blood flow without causing tissue damage.
6. Liposuction Cannulas for Harvesting Fat
Fat grafting to provide support to surrounding tissues can be required in some transplants, including pancreas or kidney transplantation. Liposuction cannulas allow surgeons to harvest adipose tissue safely and effectively.

7. Cryopreservation and Organ Transport Instruments
Keeping an organ viable before transplant is critical. Organ preservation solutions and perfusion pumps keep the organ oxygenated and functional while being transported. Specialized organ preservation bags or liquid nitrogen’s advanced cooling processes keep donor organs viable.
How New Surgical Devices Improve Organ Viability and Patient Recovery
New surgical equipment directly impacts the success rate of transplants. This is how:
1. Minimizing Trauma to the Donor Organ
Microinstruments, electric scalpels, and electrosurgical instruments enable surgeons to work with minimal trauma on organs. Swelling is reduced, tissue is less harmed, and the risk of rejection is removed.
2. Improving Surgical Accuracy
Utilization of microsurgical equipment to reattach small nerves and vessels guarantees the organ functions with a better supply of blood, reducing risks like ischemia (insufficient oxygenation).
3. Minimizing Surgical Time
Bone saws with high speeds, self-retaining retractors, and robot-assisted technology make surgery less time-consuming, minimizing the period the organ remains outside the body. This enhances the possibility of a successful transplant.
4. Avoiding Infection Risk
Surgical equipment for single-use or sterilizable use maintains a sterile environment, preventing post-operative infection and ease of healing of the patient.
5. Improved Postoperative Healing
The adoption of minimally invasive devices such as laparoscopic trocars and robotic surgery instruments leads to fewer cuts, faster recovery, and a shorter hospital stay.
The Future of Transplant Surgeries and Instrumentation
Organ transplantation as a medical specialization is seeing a swift development with advances in surgery instruments and techniques with technology. Some of the future developments are:
- 3D-Printed Surgical Instruments: Customized for individuals, they optimize precision and reduce waste.
- Robotic-Assisted Transplant: Robotic procedures increase dexterity and precision to enable less-invasive surgeries.
- Artificial and Bioengineered Organs: The creation of tissue-engineered tissues and 3D-printed organs has the potential to transform transplantation in the future.
- Enhanced Organ Preservation Techniques: New technologies like normothermic perfusion (keeping the organ warm and functional) are improving transplant success rates.
Conclusion
Organ transplant success also depends not only on skilled surgeons but also on the advanced equipment they use. Better surgical tools extend the viability of donor organs, reduce complications, and enable quicker patient recovery. The transplant procedure will become more efficient and save millions of lives worldwide as technology improves.
At Hasni Surgical, we pride ourselves on providing high-quality, precision-crafted surgical instruments that meet transplant surgeons’ stringent demands. From microvascular forceps to bone saws to trocars, our instruments help provide safer, more successful transplant procedures.
To find out more about our range of surgical instruments, go online or by phone today!
