4 Powerful Surgical Tools against Obesity: Overview of Bariatric Appliances
February 1, 2025 2025-02-01 11:304 Powerful Surgical Tools against Obesity: Overview of Bariatric Appliances

4 Powerful Surgical Tools against Obesity: Overview of Bariatric Appliances
Obesity is one of the most critical health issues all over the globe, bringing with it many diseases. The condition encompasses the state of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and sleep apnea.
As lifestyle changes and non-invasive treatments are usually unable to meet the needs of obese patients, bariatric surgery has been a helpful treatment.
Among the most commonly performed bariatric surgeries are gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, which require specialized surgical tools to ensure precision, safety, and the best possible outcome for the patient.
In this blog, we delve into the critical role bariatric surgical tools play in these life-changing surgeries, detailing the tools used and their contribution to combating obesity and its related diseases.
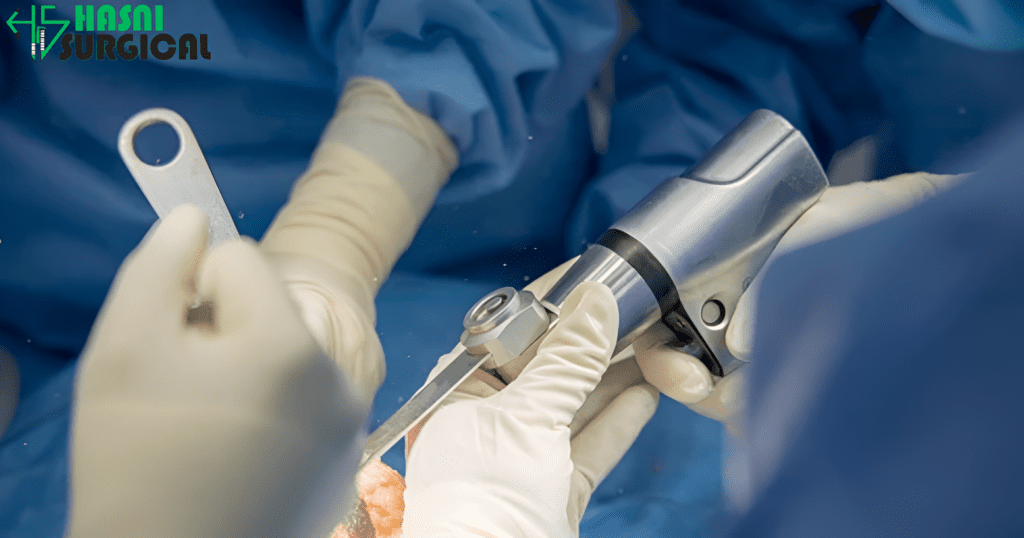
Understanding Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is a surgical procedure aimed at either reducing the size of the stomach or rearranging the digestive tract to trap food and absorption of nutrients. The two types are gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) and sleeve gastrectomy. Both of these are performed as laparoscopic surgery.
GASTRIC BYPASS: A smaller stomach pouch is created but directly connected to the small intestine. A very large portion of the digestive tract is bypassed.
Sleeve Gastrectomy: Around 75 to 80 percent of the stomach is removed in this procedure. This leaves the banana-shaped tube or “sleeve,” which limits how much food intake will be held.
Both operations demand delicate and precise execution that focuses on requiring dependable and innovative surgical instruments.
Basic Bariatric Surgical tools
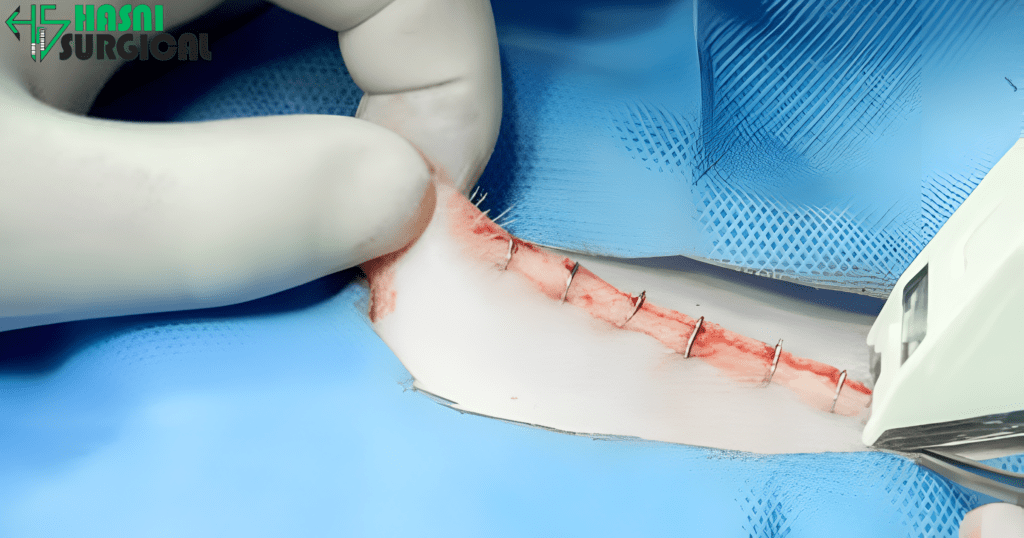
1. Laparoscopic Tools
Most bariatric surgeries are laparoscopic. That is, a number of small incisions instead of one big incision are used. This reduces scarring, recovery time, and complications. Some of the major laparoscopic instruments include:
- Trocars: These are hollow tubes placed through the abdominal wall to make a pathway for other instruments. These come in different sizes, but in the case of bariatric surgery, bigger trocars are sometimes necessary to accommodate specific equipment.
- Laparoscopic Graspers: These instruments grasp and hold tissues for surgery. This helps the surgeon achieve great precision with no tissue damage.
- Laparoscopic Scissors: These cut tissues during the procedure, for instance, while changing the stomach’s shape in sleeve gastrectomy or while forming the small pouch in gastric bypass.
- Electrosurgical Instruments: These devices help in the simultaneous cutting and coagulation of tissues with reduced blood loss.

2. Stapling Instruments
Stapling instruments are needed in bariatric surgery for the purpose of ensuring that the connection made is tight and without leakages.
- Linear staplers: This instrument separates and cuts tissue by stapling to multiple rows. It is often used when dividing the stomach in gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy.
- Circular Staplers: In making the gastrojejunostomy, connecting the stomach pouch and the small intestine in gastric bypass, circular staplers are used.
- Reinforcement Materials: Reinforcement materials will often be biologic or synthetic materials used within the stapled area to improve the chances for a staple line that is tight and leakless.
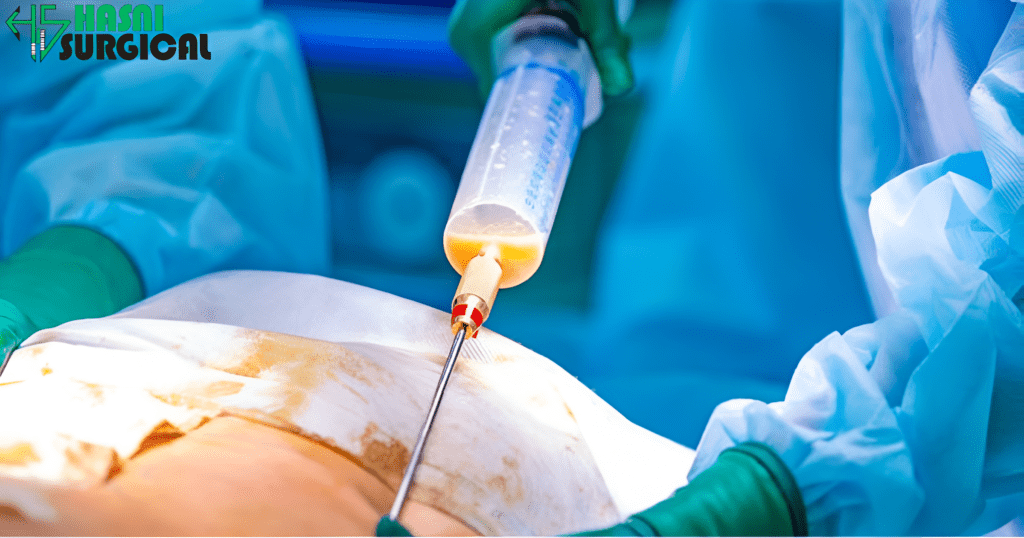
3. Energy Devices
Tissue dissecting and coagulating are achieved using energy devices to help avoid blood loss during surgery.
- Ultrasonic Energy Devices: They work by disrupting tissues with ultrasonic vibrations, cutting tissues, and coagulating the blood vessels to allow for precise and controlled dissection.
- Advanced Bipolar Devices: Bipolar devices cause simultaneous cutting and coagulation with the intention of ensuring hemostasis while minimizing thermal damage adjacent to the tissues.
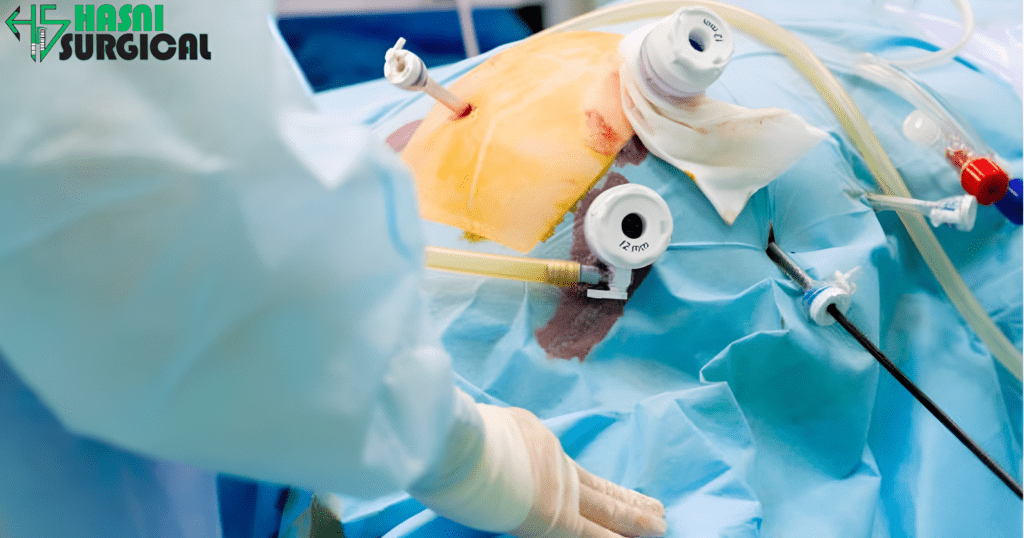
4. Suturing Devices
While staplers become almost omnipresent, a few areas in the surgery will still need to be hand-sutured for added security:
- Laparoscopic Suturing Devices: These help perform close sutures in tight places with the assurance that tissues are closed securely.
- Barbed Sutures: Self-anchoring sutures have eliminated the tying of knots, which saves time and significantly enhances the surgery’s efficiency.
5. Dedicated Retraction Devices
Bariatric surgery involves retraction of the liver for access to the stomach:
- Liver Retractors: These lift and retract the liver without trauma, ensuring adequate visualization for the surgeon.
The Role of Bariatric Surgery in Obesity Management
Obesity is a complex condition influenced by genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. For people with a BMI over 40 or with a BMI between 35 and 40 and any one of several obesity-related health conditions, bariatric surgery can be an established solution for patients after failure of other interventions.
Health Benefits of Bariatric Surgery:
- Weight Loss: The reduction in excess body weight after surgery can range from 50% to 70% within the first two years of surgery.
- Diabetes Remission: There is improved insulin sensitivity and changes in levels of gut hormones, and this often leads to remission in most patients suffering from type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Health: Bariatric surgery minimizes the chance of heart disease and stroke from occurrence by improving cholesterol levels and lowering the blood pressure.
- Improved Mobility: Severe reduction in weight diminishes joint pain and increases physical activities.
- Psychological Benefits: Patients often report improved self-esteem, reduced depression, and better quality of life.
Advances in Bariatric Surgical Instruments
Bariatric surgery is constantly evolving, and advances in surgical instruments are key to better outcomes:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems give surgeons more precision and dexterity, which reduces complications and shortens recovery times.
- Smaller, More Ergonomic Instruments: The development of lightweight and ergonomic tools minimizes surgeon fatigue and enhances precision during long procedures.
- Leak-detecting technologies: Tools that are developed to detect staple line leaks in real time, thereby reducing postoperative complications.
Conclusion
The outcomes of bariatric surgery operations, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, significantly rely on a surgeon’s qualifications and usage of good-quality, dependable instruments. The use of trocars, staplers, and energy devices, as well as different types of suture instruments, allows performing surgery exactly and safely, changing patients’ lives and alleviating obesity and associated illness.
Advances in technology improve the future aspects of bariatric surgery to look brighter as smarter tools, which help make surgeons work more efficiently in performing life-saving procedures, become safer and increasingly available to most patients worldwide.
